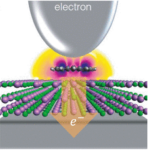
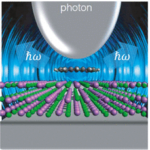
Leaders: Andrei G. Borisov and François Aguillon
The main research effort in recent years has been to use TDDFT and classical approaches to study quantum effects such as non-local screening and (possibly inelastic) tunneling in plasmonics.
Coupling light with plasmons, collective excitations of conduction electrons in metals, allows to control and enhance optical fields over nanometric distances, much smaller than the optical wavelength. We have been able to establish the role played by non-local screening, electron propagation, and especially by electron tunneling in determining the linear and non-linear optical response of plasmonic systems.
Subsequently, the idea is to study how these quantum effects can be used for active electrical control of plasmon modes. This paves the way for optoelectronic devices at the nanometric scale.
Techniques: TDDFT, ab initio calculations.
News:
— Recently available on arXiv: “Roadmap on Nonlocality in Photonic Materials and Metamaterials“: Nonlocality and related concepts play a critical role in defining the ultimate limits of what is possible in optics, photonics, and wave physics. This Roadmap aims to survey the most exciting developments in nonlocal photonic materials, highlight new opportunities and open challenges, and chart new pathways that will drive this emerging field forward, toward new scientific discoveries and technological advancements.
Highlights:
Confined bulk plasmons excited by swift electrons: A first-principles study
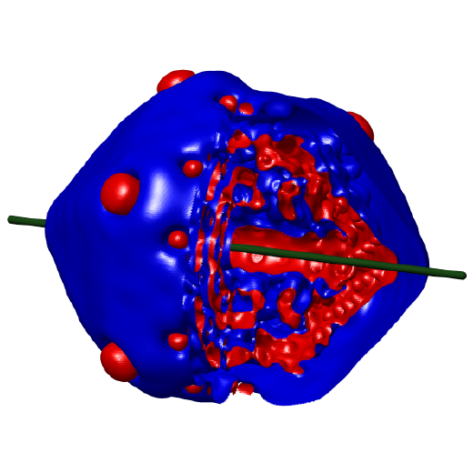
Despite the experimental observation of confined bulk plasmons (CBPs) in metallic nanostructures using electron energy-loss spectroscopy (EELS), there is still limited theoretical understanding of their resonance structure when excited by penetrating electron beams. In this work, we use atomistic ab initio time-dependent density functional theory (TDDFT) to perform a first-principles study of the excitation of CBPs induced by swift electrons. Our results represent a significant step forward in the exploration of plasmonic signatures in EELS of metallic nanoparticles.
Article : Bruno Candelas, Mattin Urbieta, Antton Babaze, Eduardo Ogando, Andrei G. Borisov, Nerea Zabala & Javier Aizpurua, “Ab Initio Atomistic Characterization of Confined Bulk and Bennett Plasmons in Metallic Nanoparticles as Probed by Penetrating Electrons”, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 16, XXX, 2965–2971 (2025), pdf
A scanning fluorescent nanoprobe based on a single molecule suspended at the tip of an STM
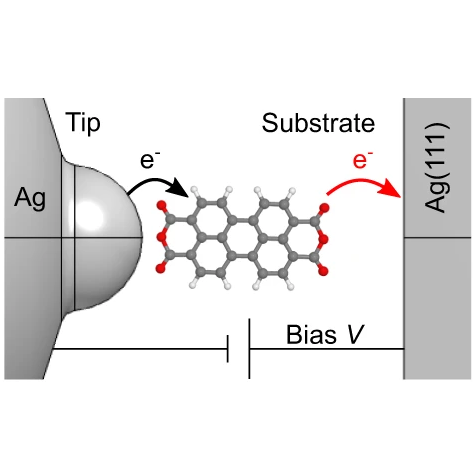
The plasmonic tip of an STM is functionalized with a single fluorescent molecule and scanned on a plasmonic substrate. Tunneling current flowing through the tip-molecule-substrate junction generates a spectrally narrow light emission corresponding to the fluorescence of the negatively charged molecule suspended on the tip apex. We demonstrate that the spectral width of the emission peak can be used as a probe of the exciton-plasmon coupling strength and that the energy of the emitted photons is governed by the interactions of the molecule with its environment.
Article : Niklas Friedrich, Anna Rosławska, Xabier Arrieta, Katharina Kaiser, Michelangelo Romeo, Eric Le Moal, Fabrice Scheurer, Javier Aizpurua, Andrei G. Borisov, Tomáš Neuman & Guillaume Schull, “Fluorescence from a single-molecule probe directly attached to a plasmonic STM tip”, Nat. Commun. 15, 9733 (2024), pdf
Graphene nanostructures have a nonlinear response to polarized light that is very different from that of macroscopic graphene.
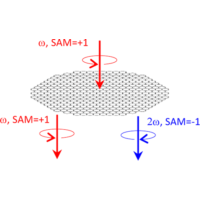
Using the tight-binding approximation and the time-dependent density matrix approach, we theoretically describe the nonlinear response of plasmonic graphene nanostructures to circularly polarized light. The intensity and polarization of the emitted harmonics depend on the symmetry of the system. For nanomaterials comprising thousands of carbon atoms, it is the symmetry of the carbon atom arrangement at the atomic scale that determines the nonlinear response. Therefore, it could be very different from the nonlinear response predicted using the macroscopic geometry. We show that symmetry breaking by lattice defects strongly affects the nonlinear response of graphene nanomaterials to circularly polarized light. Our work extends theoretical studies of the nonlinear optical properties of graphene nanomaterials to spin-carrying light beams.
Article : François Aguillon et Andrei G. Borisov, “Nonlinear Response of Nanostructured Graphene to Circularly Polarized Light”, J. Phys. Chem. C 128, 16576 (2024), pdf
Publications (since 2020) :
Model description of electron transfer between PTCDA molecule and metal surface upon molecular adsorption and STM manipulation, A. G. Borisov, Phys. Rev. B 110 (7), 075413 (2024), pdf
Nonlinear Optical Response of a Plasmonic Nanoantenna to Circularly Polarized Light: Rotation of Multipolar Charge Density and Near-Field Spin Angular Momentum Inversion, M. Quijada, A. Babaze, J. Aizpurua, A. G. Borisov, ACS Photonics 10 (11), 3963-3975 (2023), pdf
Dispersive surface-response formalism to address nonlocality in extreme plasmonic field confinement, A. Babaze, T. Neuman, R. Esteban, J. Aizpurua, A. G. Borisov, Nanophotonics 12 (16), 3277-3289 (2023), pdf
Atomic-Scale Defects Might Determine the Second Harmonic Generation from Plasmonic Graphene Nanostructures, F. Aguillon, A. G. Borisov, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 14 (1), 238-244 (2023), pdf
Quantum surface effects in the electromagnetic coupling between a quantum emitter and a plasmonic nanoantenna: time-dependent density functional theory vs. semiclassical Feibelman approach, A. Babaze, E. Ogando, P. E. Stamatopoulou, C. Tserkezis, N. A. Mortensen, J. Aizpurua, A. G. Borisov, R. Esteban, Opt. Express 30 (12), 21159-21183 (2022), pdf
Mapping Lamb, Stark and Purcell effects at a chromophore-picocavity junction with hyper-resolved fluorescence microscopy, A. Roslawska, T. Neuman, B. Doppagne, A. G. Borisov, M. Romeo, F. Scheurer, J. Aizpurua, G. Schull, Phys. Rev. X 12, 011012 (2022), pdf
Time-dependent density functional theory calculations of electronic friction in non-homogeneous media, N. E. Koval, D. Sánchez-Portal, A. G. Borisov, R. D. Muiño, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 24 (34), 20239-20248 (2022), pdf
Atomic-scale control of plasmon modes in graphene nanoribbons, F. Aguillon, D. C. Marinica, A. G. Borisov, Phys. Rev. B 105 (8), L081401 (2022), pdf
Effect of a Dielectric Spacer on Electronic and Electromagnetic Interactions at Play in Molecular Exciton Decay at Surfaces and in Plasmonic Gaps, F Aguilar-Galindo, M Zapata-Herrera, S Díaz-Tendero, J Aizpurua, A. G. Borisov, ACS Photonics 8 (12), 3495-3505 (2021), pdf
Plasmons in Graphene Nanostructures with Point Defects and Impurities, F Aguillon, DC Marinica, AG Borisov, J. Phys. Chem. C 125 (39), 21503-21510 (2021), pdf
Electronic Exciton–Plasmon Coupling in a Nanocavity Beyond the Electromagnetic Interaction Picture, A Babaze, R Esteban, AG Borisov, J Aizpurua, Nano Letters 21 (19), 8466-8473 (2021), pdf
Molecule Detection with Graphene Dimer Nanoantennas, F Aguillon, DC Marinica, AG Borisov, The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 124 (51), 28210-28219 (2020), pdf
Probing the radiative electromagnetic local density of states in nanostructures with a scanning tunneling microscope, S Cao, M Zapata-Herrera, A Campos, E Le Moal, S Marguet, G Dujardin, M Kociak, J Aizpurua, AG Borisov, E Boer-Duchemin, ACS Photonics 7 (5), 1280-1289 (2020), pdf
Second-Harmonic Generation from a Quantum Emitter Coupled to a Metallic Nanoantenna, A Babaze, R Esteban, J Aizpurua, AG Borisov, ACS Photonics 7 (3), 701-713 (2020), pdf